
Skylo Launches Direct-to-Device Connectivity Using Qualcomm's Snapdragon X80 5G Modem
Innovation
Paikan Begzad
13 September 2024
01 August 2024
|
Paikan Begzad
Summary
Summary
Google is spotlighting its latest advancements in database technology at its Cloud Next conference in Tokyo. This year, the focus is on optimizing databases for AI workloads, aligning with the industry's growing emphasis on artificial intelligence in 2024. Key updates include enhancements to the Spanner SQL database, now featuring graph and vector search capabilities, along with improved full-text search functions.
In addition, Google is introducing Gemini-powered features in BigQuery and Looker to facilitate data engineering, analysis, governance, and security tasks. This move underscores the importance of generative AI to enterprise success, though many businesses still struggle with managing their data effectively.
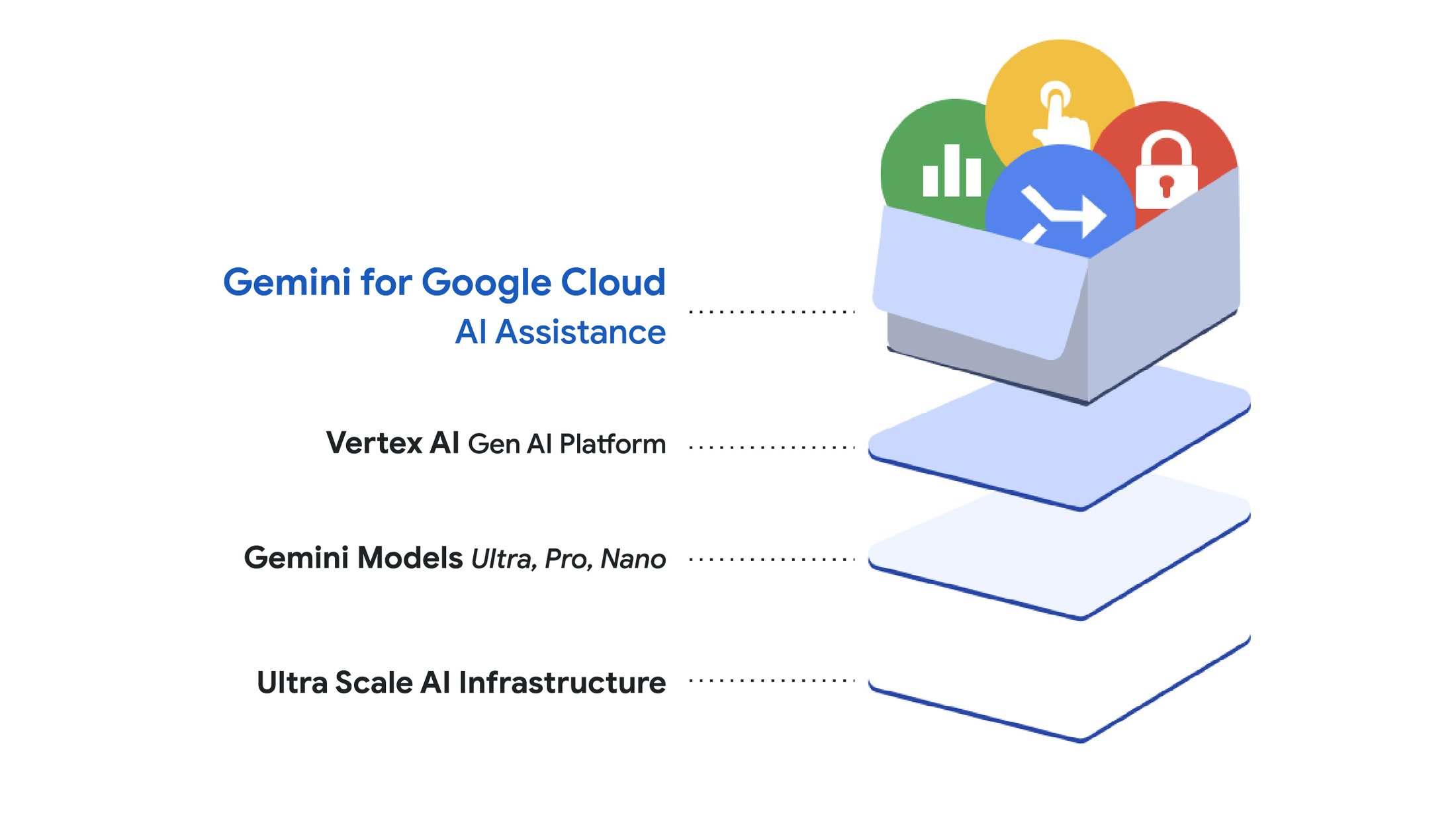
Gerrit Kazmaier, Google’s VP and GM for Database, Data Analytics, and Looker, emphasized the need for enterprises to consolidate their data from various silos and islands into a unified multimodal data platform. This platform must handle both structured and unstructured data, integrating data at rest with real-time data processing to leverage generative AI's full potential.
Spanner, a key component of Google’s infrastructure supporting services like Search, Gmail, and YouTube, now includes features essential for enriching enterprise data and integrating it into GenAI applications. The new graph capabilities, based on the GraphQL standard, enable retrieval augmented generation (RAG) to enhance GenAI applications.
Google’s VP and GM for Databases, Andi Gutmans, highlighted the expansion of Spanner’s capabilities to support operational GenAI apps, with new features like graph, full-text, and vector search powered by Google’s ScaNN algorithm. These additions transform Spanner into a multi-model database with intelligent capabilities for AI-enabled applications.
Alongside these AI-focused updates, Google introduces a new pricing model for Spanner, termed “Spanner editions,” offering tier-based pricing for greater flexibility. Additionally, Bigtable, Google’s NoSQL database, now supports SQL queries via GoogleSQL, simplifying usage for developers with about 100 SQL functions available.
Google Cloud also offers support for Oracle Exadata and Autonomous database services within its data centers, facilitating seamless integration with Oracle Cloud applications. This update ensures more workloads on Google Cloud while maintaining Oracle’s licensing revenue.
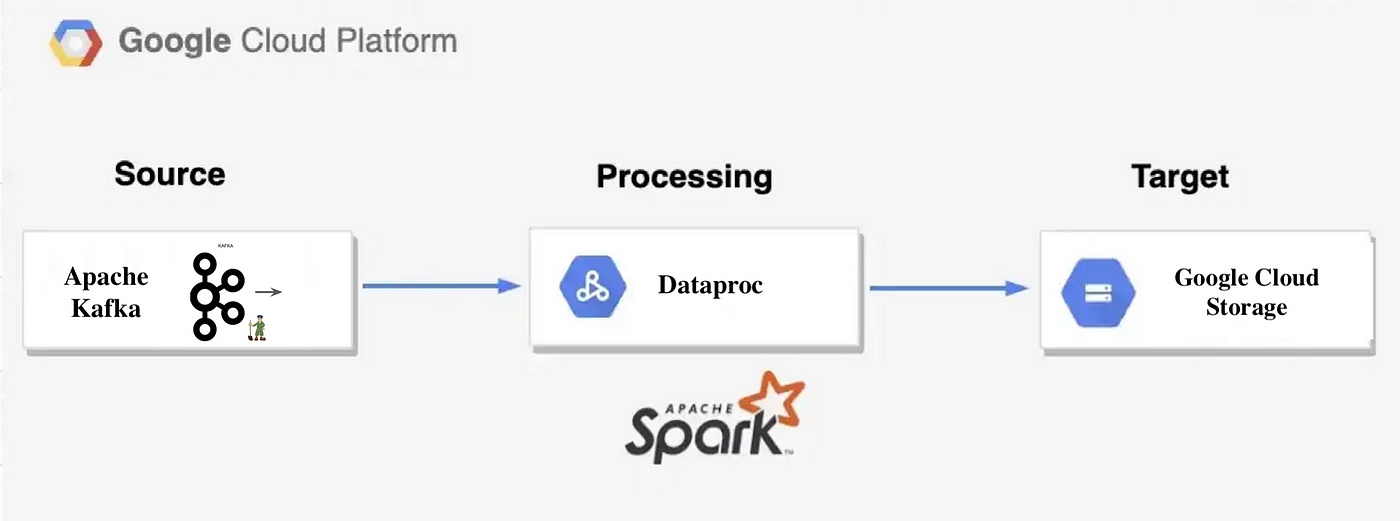
Further, Google Cloud now supports open-source Apache Spark and Kafka for data streaming and processing, alongside real-time streaming from Analytics Hub, enhancing data sharing between organizations securely.

Innovation
Paikan Begzad
13 September 2024
Innovation
Paikan Begzad
13 September 2024

Innovation
Paikan Begzad
10 September 2024

Innovation
Paikan Begzad
08 September 2024