Technology News
The Comprehensive Guide to Leveraging Big Data for Business Success
24 August 2024
|
Zaker Adham
Big data refers to the vast collection of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that businesses gather to extract valuable insights and information. It plays a crucial role in advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and machine learning projects.
Modern organizations increasingly rely on systems designed to process and store big data, integrating these with analytics tools to gain meaningful insights. The defining characteristics of big data are often summed up by the "three V's":
- Volume: The sheer amount of data collected.
- Variety: The diverse types of data stored.
- Velocity: The rapid speed at which data is generated and processed.
Initially identified by Doug Laney in 2001, these three V’s were later popularized by Gartner. Over time, additional V’s, such as Veracity, Value, and Variability, have been added to describe the complexities of big data.
Big data systems often involve massive datasets, ranging from terabytes to petabytes and even exabytes. These data points accumulate over time, making the management and analysis of big data a significant challenge and opportunity for businesses.
The Importance and Applications of Big Data
Businesses that effectively harness big data can significantly enhance their operational efficiency, customer service, and marketing efforts. By leveraging big data, companies can make quicker, more informed decisions, offering a competitive edge in the marketplace.
For instance, by analyzing customer data, businesses can refine their marketing strategies, tailor promotions, and increase engagement and conversion rates. Both historical and real-time data can be analyzed to understand consumer preferences, enabling businesses to respond more effectively to customer needs.
In the healthcare sector, big data is instrumental in identifying disease patterns and risk factors. Medical professionals use it to improve diagnostic accuracy and monitor public health threats. Similarly, big data helps industries like oil and gas, financial services, manufacturing, and government agencies optimize operations, manage risks, and improve service delivery.
Examples and Sources of Big Data
Big data originates from various sources, including transaction systems, customer databases, documents, emails, and social media. Machine-generated data, such as server logs and sensor data from IoT devices, also contribute significantly to big data environments.
In addition to internal data, organizations often incorporate external data sources, such as financial markets, weather conditions, and geographic information, to enrich their big data applications. Streaming data, including images, videos, and audio files, is another growing aspect of big data.
Breaking Down the V's of Big Data: Volume, Variety, and Velocity
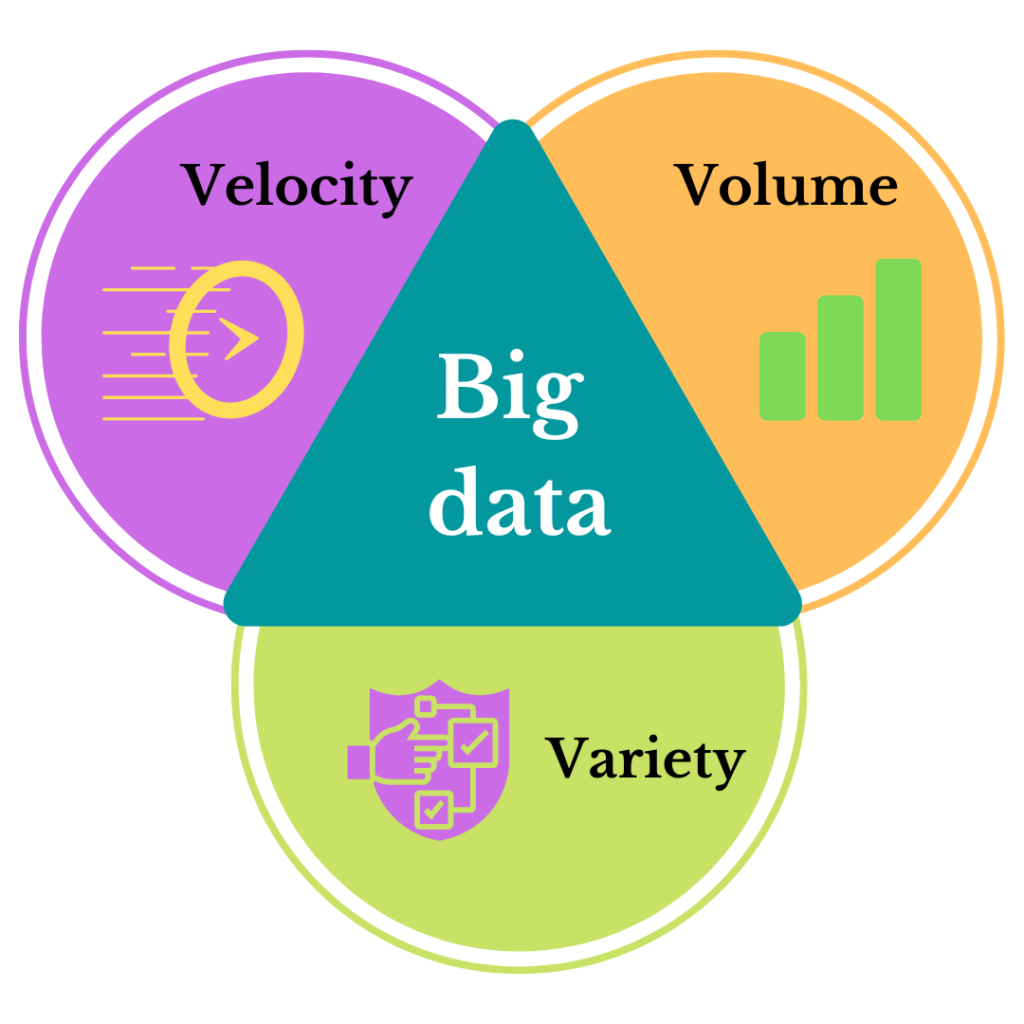
- Volume: Big data environments typically handle large quantities of data generated from sources like clickstreams and system logs.
- Variety: Big data includes structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data types, such as financial records, multimedia files, and web server logs.
- Velocity: Data in big data systems is often processed in real-time or near-real-time, a critical factor as analytics extend into machine learning and AI.
Additional Characteristics: Veracity, Value, and Variability
- Veracity: Ensuring data accuracy is crucial. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed analysis and poor decision-making.
- Value: Not all collected data holds value. Organizations must filter and utilize data relevant to their business goals.
- Variability: Data variability refers to the inconsistency in data formats and meanings, complicating data management and analysis.
Storage, Processing, and Analytics in Big Data
Big data is frequently stored in data lakes, which can handle various data types and are built on platforms like Hadoop clusters or cloud-based services. Processing big data requires substantial computing power, often provided by clustered systems using technologies like Hadoop and Spark.

The cloud is a popular choice for hosting big data systems due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness. Businesses only pay for the storage and compute time they use, making it a flexible solution for big data analytics.
Big Data Management Technologies and Benefits
Organizations using big data effectively can achieve enhanced decision-making, better customer insights, cost savings, and even positive social impacts. However, managing big data comes with challenges, including architecture design, skill requirements, and data integration.
Emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, improved cloud storage, and quantum computing are poised to further influence how businesses collect and utilize big data in the future.